
miniDOT Used to Understand Metabolism of Steppe Rivers
July 12, 2018
Cyclops-7 Logger Traces Fluorescein in Nepal
March 4, 2019Creating Models to Better Understand Lagoons
Project Details
- PRODUCT(S): miniDOT® Logger
- APPLICATION: Coastal / Ocean
- PARAMETER: Carbon Dioxide, Oxygen, pH
- LOCATION: Agua Hedionda Lagoon in Carlsbad, California
- ORGANIZATION: Scripps Institution of Oceanography
- RECOGNITION: Taylor Wirth, R&D Engineer 1

Case Study Description
For the last several years researchers from Scripps Institution of Oceanography have been running a shore-based seawater CO2 and pH monitoring system in the Agua Hedionda Lagoon in Carlsbad, California next to the Carlsbad Aquafarm.
Their goal is to create a model of the entire lagoon to estimate the effects the lagoon has on carbon levels, temperature and human impacts. In order to characterize the entire 3-part lagoon they have built 3 mini-moorings. These moorings have been in the water since August 2018. Each is in about 9 meters of water and contains:
- A surface float with a cell modem to transmit live data
- A sensor package measuring pH, oxygen, temperature, salinity at depth
- A PME miniDOT logger at the surface
There is a mooring currently in the Pacific Ocean right outside of the lagoon, one in the outer lagoon (closest to the ocean near the Aquafarm) and one in the middle of the lagoon. The map below shows these three different locations in yellow as well as the shore-based system in pink.
The shore-based system is a flow through system and contains a “Burke-o-Lator” developed by Burke Hales at Oregon State University and is uploaded in near real time via IPACOA. The system has been in use since 2015; over the years, researchers have added the means to record pH and salinity. In total, it now records pCO2, TCO2, pH and salinity. Seawater is pumped from the lagoon to the shore station and measurements are autonomously conducted twenty-four hours a day, seven days a week.
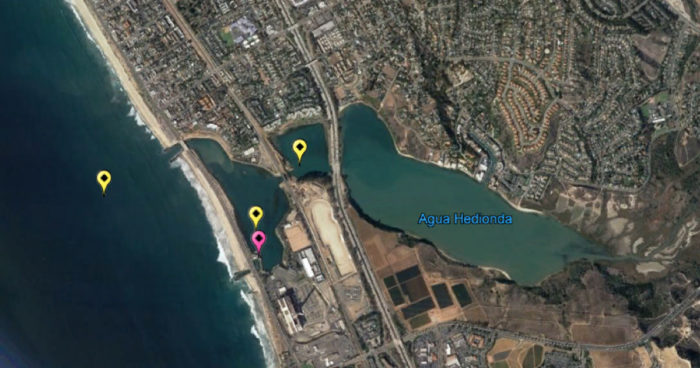
Modeling multiple factors
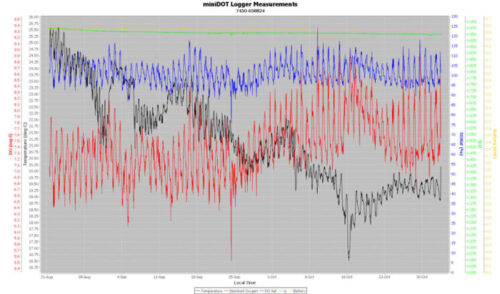
There are so many factors at play in creating a model of the lagoon (tidal, fresh water input from rain events, pollution from nearby housing and agriculture, recreation, aquafarming, dredging etc.) that the researchers need a dispersed data set from different parts of the lagoon and at different depths.
The use of the PME miniDOTs at the surface, alongside oxygen sensors at depth, create a depth range to better understand the relationship of each part of the lagoon relative to each other and its inputs. From this model, researchers will be able to estimate the effects the lagoon has on carbon levels, temperature and human impacts.
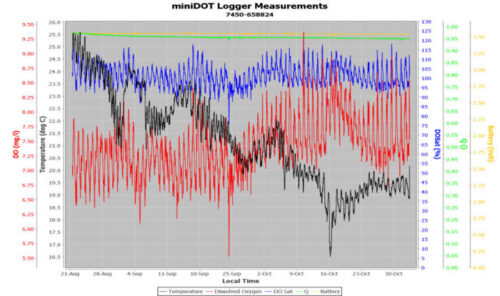 .
. 
Product Description
The miniDOT® Logger is a completely submersible instrument that logs dissolved oxygen and temperature measurements. Data is recorded on the internal SD card and operational functions, like setting time and sample intervals, can be accomplished via USB cable. The oxygen sensor is an optode that measures dissolved oxygen concentration in water through a fluorescence method. The miniDOT® can withstand temperatures ranging from 0 – 35°C with a depth rating of 300 meters.

